09-27-16 -- 'Billy' - Judy Mikovits - Gregg Tivnan -- (MP3'S & VIDEO LOADED)
Hour 1 - 3
OTHER METHODS TO CONTRIBUTE TO FREEDOM'S PHOENIX (INCLUDING PAYPAL/CREDIT CARDS) CLICK HERE
Hour 1&2 -- 'Billy' (local activist; Kratom advocate) comes in studio to talk about Kratom, what it is, and how you can use it medicinally for better health.Gregg Tivnan (friend and libertarian activist from Missouri) joins the conversation
Hour 3 - Dr. Judy Mikovits, PhD (molecular biologist) provides and update on Vaccines and Vaccinations. Gregg Tivnan (friend and libertarian activist from Missouri) joins the conversation
CALL IN TO SHOW: 602-264-2800
-30-
 Feature Article • Global Edition Feature Article • Global EditionFreedom's Phoenix Declare Your Independence APP now on Google Play Donna Hancock Listen to any recent show of "Declare Your Independence" at the click of a button! |

September 27th, 2016
Declare Your Independence with Ernest Hancock
on LRN.FM / Monday - Friday
9 a.m. - Noon (EST)
Studio Line: 602-264-2800
Hour 1
2016-09-27 Hour 1 Billy Kratom, Gregg Tivnan from Ernest Hancock on Vimeo.
'Billy' - In Studio
Billy talks about Kratom, it's uses, and why the DEA wants to classify it as a Schedule 1 substance
Webpage:
https://www.facebook.com/groups/177381892687839/
Gregg Tivnan (friend and libertarian activist from Missouri) joins the conversation
===============================
Congress Calls Out DEA For Unilateral Move To Expand The War On Drugs
http://www.huffingtonpost.com/entry/congress-kratom-dea-letter_us_57e93743e4b0e28b2b54fe36
Members of Congress are urging the federal government to delay a decision to ban the herbal supplement kratom.
09/26/2016 04:30 pm ET |
A bipartisan group of House lawmakers are asking the Drug Enforcement Administration to reconsider its decision to place the herbal supplement kratom into Schedule I of the Controlled Substances Act, a move that could take effect as early as the end of the week.
In a letter on Monday, 51 representatives ? including 22 Republicans ? called on called on acting DEA Administrator Chuck Rosenberg to delay the impending ban in order to "engage consumers, researchers, and other stakeholders, in keeping with well-established protocol for such matters."
See the full letter and list of signatories below.
"This significant regulatory action was done without any opportunity for public comment from researchers, consumers, and other stakeholders," reads the letter, drafted by Reps. Mark Pocan (D-Wis.) and Matt Salmon (R-Ariz). "This hasty decision could have serious effects on consumer access and choice of an internationally recognized herbal supplement."
Pocan's office provided a copy of the letter to The Huffington Post. The lawmakers also sent a separate letter to Shaun Donovan, director of the Office of Management and Budget, asking him to halt the DEA's scheduling process to give authorities more time to determine if kratom truly belongs in Schedule I, alongside heroin and LSD. Drugs in this category are considered to have no known medical benefit and a high potential for abuse.

TAMMY ALENDER
A jar of kratom powder, made from the leaves of leaves of Mitragyna speciosa, along with a mug of kratom tea.
In a notice published in the Federal Register at the end of August, the DEA claimed that kratom, an herb made from the leaves of Mitragyna speciosa, a Southeast Asian tree related to coffee, poses an "imminent hazard to the public safety." Kratom contains two alkaloids, mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine, which appear to activate opioid receptors in the brain and reduce pain. Though most opioids have sedative qualities, kratom is a mild stimulant in low to moderate doses.
As an herbal supplement, kratom remains largely unregulated at the federal level, though law enforcement agencies have recently begun seizing shipments of kratom products, citing health concerns. Over the past few years, state lawmakers have worked ? often with the cooperation of pro-kratom organizations ? to consider age restrictions and labeling requirements, among other regulatory measures. A federal ban would put an end to such nuanced efforts.
Kratom groups estimate millions of Americans currently use kratom to treat a variety of ailments, including chronic pain anxiety, depression and opioid addiction. But because kratom hasn't been subjected to large-scale clinical trials under federal guidelines, the DEA says the herb has "no currently accepted medical use" and is therefore moving to make criminals out of the people who currently use it. The agency also raises concerns about kratom's potential for addiction and abuse.
The DEA did not give an opportunity for public comment ahead of last month's announcement, and kratom advocates and lawmakers say they weren't aware of the agency's intent until after it published the notice.
Kratom users and scientists have since aggressively opposed the DEA's move to wage war on another plant. Critics claim the agency dismissed promising anecdotal reports and emerging scientific evidence suggesting kratom may have medical benefits ? or at the very least, a low-risk profile and minimal potential for recreational abuse.
CLICK HERE for the rest of the article
Hour 2
Hour 2 -- 'Billy' (local activist; Kratom advocate) comes in studio to talk about Kratom, what it is, and how you can use it medicinally for better health. Gregg Tivnan (friend and libertarian activist from Missouri) joins the conversation
-30-
Hour 2
2016-09-27 Hour 2 Billy Kratom, Gregg Tivnan from Ernest Hancock on Vimeo.
'Billy'
In Studio
Hour 3
Hour 3 - Dr. Judy Mikovits, PhD (molecular biologist) provides and update on Vaccines and Vaccinations. Gregg Tivnan (friend and libertarian activist from Missouri) joins the conversation
-30-
Hour 3
2016-09-27 Hour 3 Judy Mikovits, Billy, Gregg Tivnan from Ernest Hancock on Vimeo.
Dr. Judy Mikovits, PhD
Judy A. Mikovits, PhD has spent her life training to be a research scientist to honor her grandfather who died of cancer when she was a teenager. Dr. Mikovits earned her BA from University of Virginia and PhD in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology from George Washington University. In her 35-year quest to understand and treat chronic diseases, she has studied immunology, natural products chemistry, epigenetics, virology and drug development. In just over twenty years she rose from an entry-level lab technician to become director of the lab of Antiviral Drug Mechanisms at the National Cancer Institute before leaving to direct the Cancer Biology program at EpiGenX Pharmaceuticals in Santa Barbara, California where she had met and married David Nolde in 2000. There in 2006, she became attracted to the plight of patients with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome and Autism. In only five years she developed the first neuroimmune institute from a concept to a reality and is primarily responsible for demonstrating the relationship between immune based inflammation and these diseases. She has published over 50 scientific papers.
Dr. Judy A. Mikovits recently founded MAR Consulting Inc. with her collaborator Dr. Frank Ruscetti.
She can be contacted at:
MAR Consulting Inc.
300 Carlsbad Village Drive
Suite 108A Box 132
Carlsbad, CA 92008or
MAR Consulting Inc. website:
Mission statement
MAR Consulting Inc., led by Drs. Frank Ruscetti and Judy A. Mikovits, seeks to understand complex and innovative biological issues to yield unbiased integrated, cutting-edge information for patients and physicians impacted by some of the most challenging chronic diseases. Utilizing their combined 75 years experience in tumor biology, immunobiology of retroviral-associated inflammatory diseases, cancer, stem cell biology, hematopoiesis, and drug development, MAR focuses on research projects, consulting (to patients doctors, academia, and industry) and lecturing without the restrictive authority of vested interest groups, following Thomas Jefferson's dictum: "Here we are not afraid to follow the truth wherever it may lead, nor to tolerate error so long as freedom is left free to combat it."
Webpage: http://www.plaguethebook.com/
On July 22, 2009, a special meeting was held with twenty-four leading scientists at the National Institutes of Health to discuss early findings that a newly discovered retrovirus was linked to chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), prostate cancer, lymphoma, and eventually neurodevelopmental disorders in children.
When Dr. Judy Mikovits finished her presentation the room was silent for a moment, then one of the scientists said, "Oh my God!" The resulting investigation would be like no other in science.
For Dr. Mikovits, a twenty-year veteran of the National Cancer Institute, this was the midpoint of a five-year journey that would start with the founding of the Whittemore-Peterson Institute for Neuro-Immune Disease at the University of Nevada, Reno, and end with her as a witness for ?the federal government against her former employer, Harvey Whittemore, for Illegal campaign contributions to U. S. Senate Majority Leader, Harry Reid.
On this journey Dr. Mikovits would face the scientific prejudices against CFS, wander into the minefield that is autism, and through it all struggle to maintain her faith in God and the profession to which she had dedicated her life. This is a story for anybody interested in the peril and promise of science at the very highest levels in our country.
Plague The Book: Teaser Trailer:
To order your copy of Plague: One Scientist's intrepid Search For the Truth about Human Retroviruses and Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, Autism, and Other Diseases Click on any of the links - Amazon.com Barnes & Noble.com IndieBound
=================================
Dr. Miskovits's Interview on the Awakening Liberty Show
Crimes Against Humanity, VAXXED Film Review, END the CDC:
Published on Jul 18, 2016
The Awakening Liberty Show with my guests Dr Judy Mikovits and Kent Heckenlively co-authors of "Plague the Book, One Scientists Intrepid Search for the Truth about Human Retroviruses and CFS, Autism and other Diseases" joined me for a charged show including a review of the film Vaxxed. On July 22, 2009, a special meeting was held with twenty-four leading scientists at the National Institutes of Health to discuss early findings that a newly discovered retrovirus (found in the vaccines and blood supply) was linked to chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), prostate cancer, lymphoma, and eventually neuro-developmental disorders (like Autism) in children. Judy's story unfolds like a Hollywood blockbuster of corruption, blackmail and diabolical evil. But this is not fiction, nor is it a theory, it is in fact, Conspiracy Reality. Characterizing the WHO (World Health Organization) as the Don of a mafioso crime syndicate, Dr Judy and Kent Heckenlively courageously expose a corruption plot so deep it's almost unimaginable! There is a war on for our Health!! Save the Babies! Educate before you Vaccinate! Please share this show and get a copy of Plague to share with family and friends. Much Love and many thanks to Dr Judy and Kent for all they are doing in these dark times!
website: www.plaguethebook.com
Listen LIVE to The Awakening Liberty Show with Sean Caron every Saturday and Sunday at 2 PM Pacific Time!
http://truthfrequencyradio.com/listen...
Become a TFR supporter with this link and 50% of your subscription goes to Awakening Liberty! Help keep TFR 100% Listener Supported http://truthfrequencyradio.com/amembe...
Awakening Liberty Show Website http://www.awakeninglibertyshow.com/
=================================
Freedom's Phoenix Vaccines and Vaccinations Category Pages for a comprehensive log on the subject: https://www.freedomsphoenix.com/Subjects/00287-LAST-vaccines-and-vaccinations.htm?Editor?EdNo=001
==================================
Judy's previous interviews on the Declare Your Independence with Ernest Hancock Radio Show:
https://www.freedomsphoenix.com/Guest-Page.htm?No=01359
===========================
Truth and Transparency Summit
Oct 14 at 7 AM to Oct 16 at 7 AM in EDT
https://www.facebook.com/events/582563235256264/?active_tab=highlights
-Friday, October 14, 2016-
Protest Rally
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
1600 Clifton Road Atlanta, GA 30329
7am to 2pm
Join health freedom activists from all over the United States and abroad as we gather at ground zero to protest the fraud, manipulation and cover-up of the most egregious medical fraud of the century.
**The Vaxxed team will also be attending with the bus!!!**
7pm - Screening of Vaxxed at the Sheraton Hotel Downtown Atlanta followed by a Q&A with the Vaxxed Team
-Saturday, October 15, 2016 - Health Education Summit
*Will be announced to those who buy the tickets*
Tentatively 1pm to 5pm
Screening of Vaxxed - TBD
-Sunday, October 16, 2016 - The Honorable Minister Louis Farrakhan at the Fox Theater at 2pm:
Purchase tickets here: tinyurl.com/FoxTicks
http://cdctruthsummit.weebly.com/
or cdctruth.info
#cdcwhistleblower #hearus #vaxxed #CDCTRUTH
===========================
Retrovirus
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Retrovirus
RetrovirusesVirus classification Genera
 |
|
| HIV retrovirus schematic of cell infection, virus production and virus structure | |
| Group: | Group VI (ssRNA-RT) |
| Order: | Unassigned |
| Family: | Retroviridae |
|
Subfamily: Orthoretrovirinae Subfamily: Spumaretrovirinae |
|
Retroviridae is a family of enveloped viruses that replicate in a host cell through the process of reverse transcription. A retrovirus is a single-stranded positive-sense RNA virus with a DNA intermediate and, as an obligate parasite, targets a host cell. Once inside the host cell cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase enzyme to produce DNA from its RNA genome — the reverse of the usual pattern, thus retro (backwards). This new DNA is then incorporated into the host cell genome by an integrase enzyme, at which point the retroviral DNA is referred to as a provirus. The host cell then treats the viral DNA as part of its own genome, translating and transcribing the viral genes along with the cell's own genes, producing the proteins required to assemble new copies of the virus. It is difficult to detect the virus until it has infected the host. At that point, the infection will persist indefinitely.
In most viruses, DNA is transcribed into RNA, and then RNA is translated into protein. However, retroviruses function differently – their RNA is reverse-transcribed into DNA, which is integrated into the host cell's genome (when it becomes a provirus), and then undergoes the usual transcription and translational processes to express the genes carried by the virus. So, the information contained in a retroviral gene is used to generate the corresponding protein via the sequence: RNA → DNA → RNA → polypeptide. This extends the fundamental process identified by Francis Crick (one gene-one peptide) in which the sequence is: DNA → RNA → peptide (proteins are made of one or more polypeptide chain; e.g. haemoglobin is a four-chain peptide).
Retroviruses are valuable research tools in molecular biology, and have been used successfully in gene delivery systems.[1]
Structure
Virions of retroviruses consist of enveloped particles about 100 nm in diameter. The virions also contain two identical single-stranded RNA molecules 7–10 kilobases in length. Although virions of different retroviruses do not have the same morphology or biology, all the virion components are very similar.[2]
The main virion components are:
Envelope: composed of lipids (obtained from the host plasma membrane during budding process) as well as glycoprotein encoded by the env gene. The retroviral envelope serves three distinct functions: protection from the extracellular environment via the lipid bilayer, enabling the retrovirus to enter/exit host cells through endosomal membrane trafficking, and the ability to directly enter cells by fusing with their membranes.
RNA: consists of a dimer RNA. It has a cap at the 5' end and a poly(A) tail at the 3' end. The RNA genome also has terminal noncoding regions, which are important in replication, and internal regions that encode virion proteins for gene expression. The 5' end includes four regions, which are R, U5, PBS, and L. The R region is a short repeated sequence at each end of the genome used during the reverse transcription to ensure correct end-to-end transfer in the growing chain. U5, on the other hand, is a short unique sequence between R and PBS. PBS (primer binding site) consists of 18 bases complementary to 3' end of tRNA primer. L region is an untranslated leader region that gives the signal for packaging of the genome RNA. The 3' end includes 3 regions, which are PPT (polypurine tract), U3, and R. The PPT is a primer for plus-strand DNA synthesis during reverse transcription. U3 is a sequence between PPT and R, which serves as a signal that the provirus can use in transcription. R is the terminal repeated sequence at 3' end.
Proteins: consisting of gag proteins, protease (PR), pol proteins, and env proteins.
Group-specific antigen (gag) proteins are major components of the viral capsid, which are about 2000–4000 copies per virion.
Protease is expressed differently in different viruses. It functions in proteolytic cleavages during virion maturation to make mature gag and pol proteins.
Pol proteins are responsible for synthesis of viral DNA and integration into host DNA after infection.
Env proteins play a role in association and entry of virions into the host cell.[3] Possessing a functional copy of an env gene is what makes retroviruses distinct from retroelements.[4] The ability of the retrovirus to bind to its target host cell using specific cell-surface receptors is given by the surface component (SU) of the Env protein, while the ability of the retrovirus to enter the cell via membrane fusion is imparted by the membrane-anchored trans-membrane component (TM). Thus it is the Env protein that enables the retrovirus to be infectious.
Multiplication
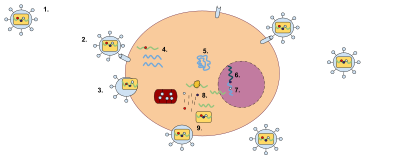
A retrovirus has a membrane containing glycoproteins, which are able to bind to a receptor protein on a host cell. There are two strands of RNA within the cell that have three enzymes: protease, reverse transcriptase, and integrase (1). The first step of replication is the binding of the glycoprotein to the receptor protein (2). Once these have been bound, the cell membrane degrades, becoming part of the host cell, and the RNA strands and enzymes enter the cell (3). Within the cell, reverse transcriptase creates a complementary strand of DNA from the retrovirus RNA and the RNA is degraded; this strand of DNA is known as cDNA (4). The cDNA is then replicated, and the two strands form a weak bond and enter the nucleus (5). Once in the nucleus, the DNA is integrated into the host cell's DNA with the help of integrase (6). This cell can either stay dormant, or RNA may be synthesized from the DNA and used to create the proteins for a new retrovirus (7). Ribosome units are used to transcribe the mRNA of the virus into the amino acid sequences which can be made into proteins in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. This step will also make viral enzymes and capsid proteins (8). Viral RNA will be made in the nucleus. These pieces are then gathered together and are pinched off of the cell membrane as a new retrovirus (9).
When retroviruses have integrated their own genome into the germ line, their genome is passed on to a following generation. These endogenous retroviruses (ERVs), contrasted with exogenous ones, now make up 5-8% of the human genome.[5] Most insertions have no known function and are often referred to as "junk DNA". However, many endogenous retroviruses play important roles in host biology, such as control of gene transcription, cell fusion during placental development in the course of the germination of an embryo, and resistance to exogenous retroviral infection. Endogenous retroviruses have also received special attention in the research of immunology-related pathologies, such as autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis, although endogenous retroviruses have not yet been proven to play any causal role in this class of disease.[6]
While transcription was classically thought to occur only from DNA to RNA, reverse transcriptase transcribes RNA into DNA. The term "retro" in retrovirus refers to this reversal (making DNA from RNA) of the central dogma of molecular biology. Reverse transcriptase activity outside of retroviruses has been found in almost all eukaryotes, enabling the generation and insertion of new copies of retrotransposons into the host genome. These inserts are transcribed by enzymes of the host into new RNA molecules that enter the cytosol. Next, some of these RNA molecules are translated into viral proteins. For example, the gag gene is translated into molecules of the capsid protein, the pol gene is translated into molecules of reverse transcriptase, and the env gene is translated into molecules of the envelope protein. It is important to note that a retrovirus must "bring" its own reverse transcriptase in its capsid, otherwise it is unable to utilize the enzymes of the infected cell to carry out the task, due to the unusual nature of producing DNA from RNA.
Industrial drugs that are designed as protease and reverse transcriptase inhibitors are made such that they target specific sites and sequences within their respective enzymes. However these drugs can quickly become ineffective due to the fact that the gene sequences that code for the protease and the reverse transcriptase quickly mutate. These changes in bases cause specific codons and sites with the enzymes to change and thereby avoid drug targeting by losing the sites that the drug actually targets.
Because reverse transcription lacks the usual proofreading of DNA replication, a retrovirus mutates very often. This enables the virus to grow resistant to antiviral pharmaceuticals quickly, and impedes the development of effective vaccines and inhibitors for the retrovirus.[7]
One difficulty faced with some retroviruses, such as the Moloney retrovirus, involves the requirement for cells to be actively dividing for transduction. As a result, cells such as neurons are very resistant to infection and transduction by retroviruses. This gives rise to a concern that insertional mutagenesis due to integration into the host genome might lead to cancer or leukemia. This is unlike Lentivirus, a genus of Retroviridae, which are able to integrate their RNA into the genome of non-dividing host cells.
Transmission
Cell-to-cell[8]
Fluids
Airborne, like the Jaagsiekte sheep retrovirus.
Provirus
This DNA can be incorporated into host genome as a provirus that can be passed on to progeny cells. The retrovirus DNA is inserted at random into the host genome. Because of this, it can be inserted into oncogenes. In this way some retroviruses can convert normal cells into cancer cells. Some provirus remains latent in the cell for a long period of time before it is activated by the change in cell environment.
Early evolution
Studies of retroviruses led to the first demonstrated synthesis of DNA from RNA templates, a fundamental mode for transferring genetic material that occurs in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. It has been speculated that the RNA to DNA transcription processes used by retroviruses may have first caused DNA to be used as genetic material. In this model, the RNA world hypothesis, cellular organisms adopted the more chemically stable DNA when retroviruses evolved to create DNA from the RNA templates.
Gene therapy
Gammaretroviral and lentiviral vectors for gene therapy have been developed that mediate stable genetic modification of treated cells by chromosomal integration of the transferred vector genomes. This technology is of use, not only for research purposes, but also for clinical gene therapy aiming at the long-term correction of genetic defects, e.g., in stem and progenitor cells. Retroviral vector particles with tropism for various target cells have been designed. Gammaretroviral and lentiviral vectors have so far been used in more than 300 clinical trials, addressing treatment options for various diseases.[1][9] Retroviral mutations can be developed to make transgenic mouse models to study various cancers and their metastatic models.
Cancer
Retroviruses that cause tumor growth include Rous sarcoma virus and Mouse mammary tumor virus. Cancer can be triggered by proto-oncogenes that were mistakenly incorporated into proviral DNA or by the disruption of cellular proto-oncogenes. Rous sarcoma virus contains the src gene that triggers tumor formation. Later it was found that a similar gene in cells is involved in cell signaling, which was most likely excised with the proviral DNA. Nontransforming viruses can randomly insert their DNA into proto-oncogenes, disrupting the expression of proteins that regulate the cell cycle. The promoter of the provirus DNA can also cause over expression of regulatory genes.
Classification
Phylogeny of Retroviruses
Exogenous
These are infectious RNA-containing viruses which are transmitted from human to human.
The following genera are included here:
Genus Alpharetrovirus; type species: Avian leukosis virus; others include Rous sarcoma virus
Genus Betaretrovirus; type species: Mouse mammary tumour virus
Genus Gammaretrovirus; type species: Murine leukemia virus; others include Feline leukemia virus
Genus Deltaretrovirus; type species: Bovine leukemia virus; others include the cancer-causing Human T-lymphotropic virus
Genus Epsilonretrovirus; type species: Walleye dermal sarcoma virus
Genus Lentivirus; type species: Human immunodeficiency virus 1; others include Simian, Feline immunodeficiency viruses
Genus Spumavirus; type species: Simian foamy virus
These were previously divided into three subfamilies (Oncovirinae, Lentivirinae, and Spumavirinae), but are now divided into two: Orthoretrovirinae and Spumaretrovirinae. The term oncovirus is now commonly used to describe a cancer-causing virus.
Retroviruses were in 2 groups of the Baltimore classification.
Group VI viruses
All members of Group VI use virally encoded reverse transcriptase, an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase, to produce DNA from the initial virion RNA genome. This DNA is often integrated into the host genome, as in the case of retroviruses and pseudoviruses, where it is replicated and transcribed by the host.
Group VI includes:
Family Metaviridae
Family Pseudoviridae
Family Retroviridae — Retroviruses, e.g. HIV
Group VII viruses
Both families in Group VII have DNA genomes contained within the invading virus particles. The DNA genome is transcribed into both mRNA, for use as a transcript in protein synthesis, and pre-genomic RNA, for use as the template during genome replication. Virally encoded reverse transcriptase uses the pre-genomic RNA as a template for the creation of genomic DNA.
Group VII includes:
Family Hepadnaviridae — e.g. Hepatitis B virus
Family Caulimoviridae — e.g. Cauliflower mosaic virus
Endogenous
Endogenous retroviruses are not formally included in this classification system, and are broadly classified into three classes, on the basis of relatedness to exogenous genera:
Class I are most similar to the gammaretroviruses
Class II are most similar to the betaretroviruses and alpharetroviruses
Class III are most similar to the spumaviruses.
Treatment
Antiretroviral drugs are medications for the treatment of infection by retroviruses, primarily HIV. Different classes of antiretroviral drugs act on different stages of the HIV life cycle. Combination of several (typically three or four) antiretroviral drugs is known as highly active anti-retroviral therapy (HAART).[10]
Treatment of veterinary retroviruses
Feline leukemia virus and Feline immunodeficiency virus infections are treated with biologics, including the only immunomodulator currently licensed for sale in the United States, Lymphocyte T-Cell Immune Modulator (LTCI).[11]
References
Kurth, Reinhard; Bannert, Norbert, eds. (2010). Retroviruses: Molecular Biology, Genomics and Pathogenesis. Horizon Scientific. ISBN 978-1-904455-55-4.
Coffin, John M. (1992). "Structure and Classification of Retroviruses". In Levy, Jay A. The Retroviridae. 1 (1st ed.). New York: Plenum. p. 20. ISBN 0-306-44074-1.
Coffin 1992, pp. 26–34
Kim FJ, Battini JL, Manel N, Sitbon M (January 2004). "Emergence of vertebrate retroviruses and envelope capture". Virology. 318 (1): 183–91. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2003.09.026. PMID 14972546.
Robert Belshaw; Pereira V; Katzourakis A; Talbot G; Paces J; Burt A; Tristem M. (April 2004). "Long-term reinfection of the human genome by endogenous retroviruses". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101 (14): 4894–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.0307800101. PMC 387345 . PMID 15044706.
. PMID 15044706.
Medstrand P, van de Lagemaat L, Dunn C, Landry J, Svenback D, Mager D (2005). "Impact of transposable elements on the evolution of mammalian gene regulation". Cytogenet Genome Res. 110 (1-4): 342–52. doi:10.1159/000084966. PMID 16093686.
Svarovskaia ES; Cheslock SR; Zhang WH; Hu WS; Pathak VK. (January 2003). "Retroviral mutation rates and reverse transcriptase fidelity.". Front Biosci. 8 (1-3): d117–34. doi:10.2741/957. PMID 12456349.
Jolly C (March 2011). "Cell-to-cell transmission of retroviruses: Innate immunity and interferon-induced restriction factors.". Virology. 411 (2): 251–9. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2010.12.031. PMC 3053447 . PMID 21247613.
. PMID 21247613.
Desport, M, ed. (2010). Lentiviruses and Macrophages: Molecular and Cellular Interactions. Caister Academic. ISBN 978-1-904455-60-8.
Haddad M, Inch C, Glazier RH, et al. (2000). "Patient support and education for promoting adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy for HIV/AIDS". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (3): CD001442. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001442. PMID 10908497.
Gingerich DA (2008). "Lymphocyte T-cell immunomodulator (LTCI): Review of the immunopharmacology of a new biologic" (PDF). Intern J Appl Res Vet Med. 6 (2): 61–8.
External links
 |
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Retroviruses. |
ViralZone A Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics resource for all viral families, providing general molecular and epidemiological information (follow links for "Retro-transcribing viruses")
Retrovirus Animation (Flash Required)
Retrovirology Scientific journal
Retrovirus life cycle chapter From Kimball's Biology (online biology textbook pages)
Coffin, John M; Hughes, Stephen H; Varmus, Harold E, eds. (1997). Retroviruses. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. ISBN 0-87969-571-4. NBK19376.
Specter, Michael (3 December 2007). "Annals of Science: Darwin's Surprise". The New Yorker.